ActivitiesGeneral Activities
JMA Continuing Medical Education (CME) Program

Lifelong learning is one of the responsibilities of physicians, who are expected to study the ever-advancing medical knowledge and skills throughout their lives to provide quality medical care to the public.
The JMA Continuing Medical Education (CME) Program was established in 1987 with the aim of developing a support system for lifelong learning among physicians. The program has been revised several times to improve and enhance the quality of the program.
The JMA assesses the achievements and learning outcomes of participation in curriculum-based courses, e-learning, experiential learning, attending and presenting at conferences, writing papers, etc. The JMA then issues a JMA Certificate of Continuing Medical Education to doctors who meet the accreditation criteria.
In addition, the JMA’s CME Program offers a number of courses, such as the Common Course for Specialists and courses that can be credited by the Japanese Society of Internal Medicine and other societies.
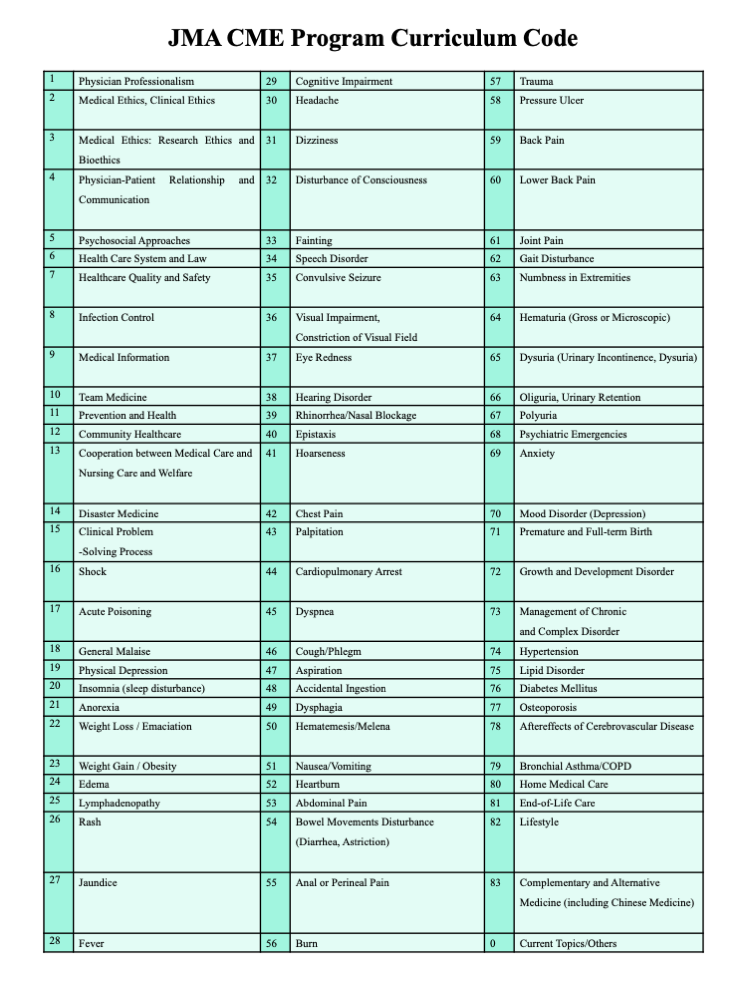
JMA Certified Occupational Physician System
In 1990, the JMA launched the Certified Occupational Physician System with the aim of improving the qualifications of occupational physicians and promoting their activities as part of community health activities.
The JMA accredited physicians who have completed at least 50 credits of basic training in occupational medicine based on a prescribed curriculum as JMA certified occupational physicians.
To renew their certificate, they must complete a minimum of 20 credits of lifelong learning in occupational medicine during the five-year period of validity.
Physicians who have completed basic training in occupational medicine under the JMA-accredited Occupational Physician System are positioned as one of the requirements to become an occupational physician under the Ordinance on Industrial Safety and Hygiene.
Prefectural medical associations act as contact points for this system, issuing training manuals and accepting various applications.
By the end of May 2022, a total of 106,809 certified occupational physicians had been trained.
JMA Certified Health and Sports Physician System
In 1991, the Japan Medical Association launched the Certified Health and Sports Physician System to train doctors who, in response to the growing interest in exercise in the local community, could provide not only medical treatment, but also medical examinations and exercise prescriptions for people who exercise, as well as guidance and advice to various exercise leaders and others.
Physicians who have completed a health and sports medicine course (25 subjects) based on a prescribed curriculum are accredited as a Japan Medical Association-Certified Health and Sports Physicians.
To renew their certificate, they must complete at least five credits of refresher training in health and sports medicine during the five-year period of validity and practice as a health and sports physician.
Prefectural medical associations act as contact points for this system and accept various applications.
By the end of May 2022, a total of 24,483 certified health and sports physicians have been trained.
JMA Pension Scheme
The JMA Pension Scheme is operated by the JMA as part of its work relating to the welfare of its members.
The Scheme was established in October 1968 with the aim of contributing to the stability of the retirement lives of members and their survivors, based on the belief that the enhancement and development of national healthcare would not be possible without the security of physicians’ livelihoods in their old age.
It has grown into one of Japan’s leading private pensions, with assets under management of over JPY 500 billion, and has become an important pillar of its member’s welfare.
The scheme has been authorized as a specified insurance business under the Insurance Business Act since April 2013 and is now operating stably as a more secure and safe pension scheme.
The scheme has many special features for JCMT members, such as the ability to freely design a pension plan to suit the member’s lifestyle.
JMA Medical Professional Liability Insurance System
The system was established in 1973 to provide insurance for members in the event of a medical accident.
Subsequently, the JMA Medical Liability Special Insurance System (voluntary subscription) was added to the system to cover high compensation for members and medical accident disputes involving physicians who are not members of the JMA.
If a civil dispute arises as a result of a member’s medical accident, the JMA, the prefectural medical associations and the insurance company shall cooperate to resolve the dispute in accordance with the decision of the Liability Review Committee in order to ensure the proper handling of the dispute.
In addition, since July 2016, compensation for the activities of industrial physicians, school physicians and others has been expanded to support the unique insurance scheme of the JMA.
In addition, in line with the Medical Accident Investigation System that came into effect in October 2015, the JMA Medical Accident Investigation Expense Insurance was launched to reimburse medical institutions for expenses incurred during in-hospital accident investigations.
Initiatives to realize medical DX
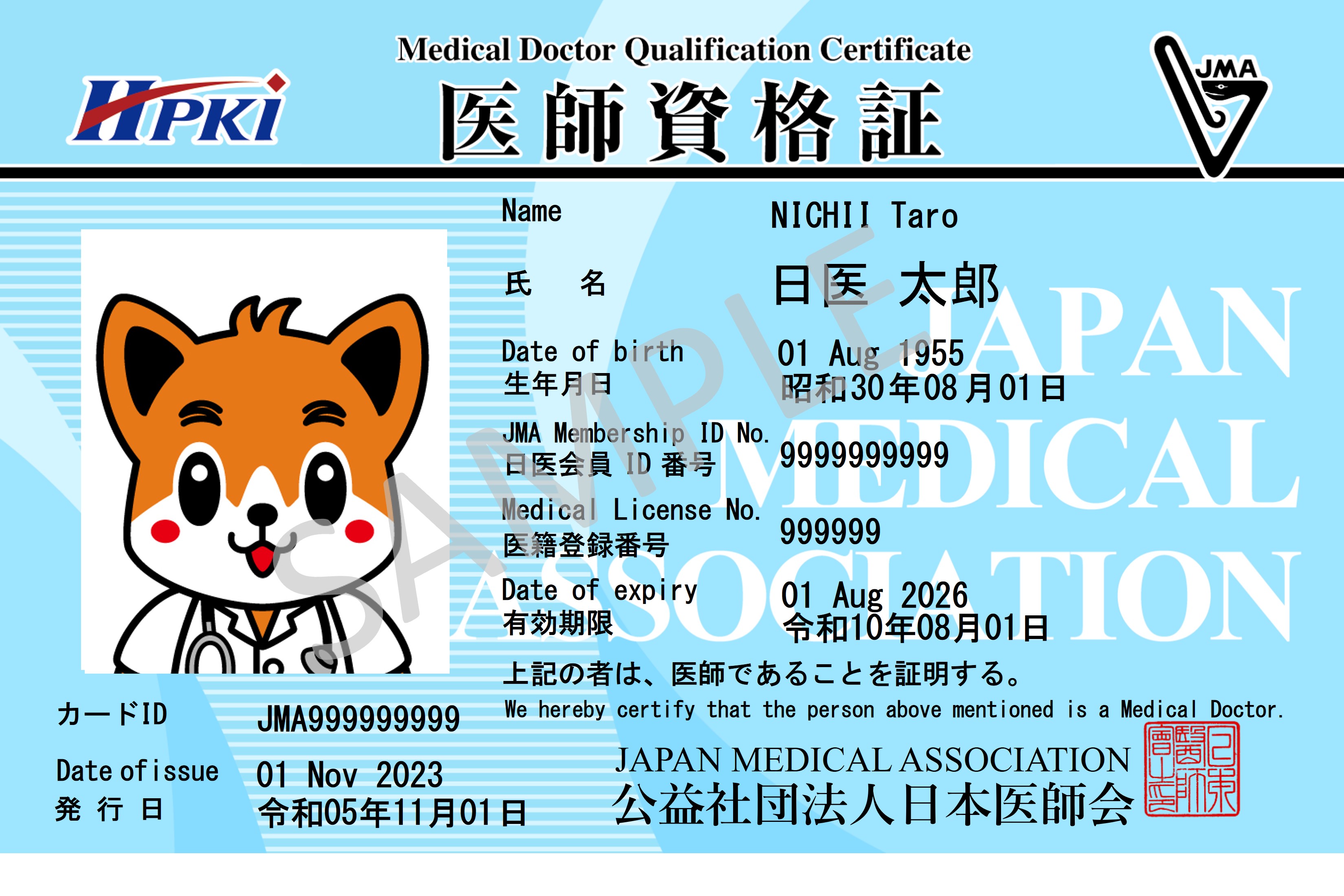
The JMA is working on the realization of IT in the medical field, including the issuance of the “Physician Qualification Certificate”, an IC card that can be used to prove a physician’s qualification on a network, under the major policy of the ‘Declaration of the IT of the JMA 2016’ issued in 2016.
IT will help to provide safer and higher-quality healthcare to the public and patients and reduce the burden on the medical frontline by improving the efficiency of operations in the medical field and promoting appropriate information linkage, etc. - in other words, further efforts will be made to realize digital transformation (DX) in the healthcare sector.
JMA Certificate Authority (JMACA)

The Japan Medical Association (JMA) established the JMA Certificate Authority (JMACA) in May 2013. The primary purpose was to issue and utilize the “Physician Certificate of Qualification” (HPKI Card, with a built-in IC chip) to certify medical qualifications in accordance with the Healthcare Public Key Infrastructure (HPKI) for Health and Medical Welfare of the Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare.
Apart from its core function of issuing the HPKI Card, the JMACA is also actively involved in the development and dissemination of standard applications for its use.
In addition, JMACA supports the promotion of the use of the HPKI Card when building a regional cooperation infrastructure using IT, and is implementing a project to develop a safe and secure medical IT infrastructure.
Furthermore, JMACA is engaged in a project of providing a system that contributes to the improvement of convenience for members who use the HPKI Card.
JMA Doctor Support Center


The JMA has been designated by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare to establish the “Doctor Support Center.” As part of the Center’s “Support Program for Women Physicians”, the following programs and services are conducted to promote the active participation of women physicians and others.
Employment Placement Services (Service name: JMA Doctor Bank*)
The “JMA Doctor Bank” provides employment placement services that integrate the “Support Program for Women Physicians (Employment Support for Women Physicians and Others)” and the “Regional Matching Program to Correct the Maldistribution of Physicians.” (*The name was changed from “JMA Woman Doctor Bank” to “JMA Doctor Bank” on November 1, 2025.)
Reemployment Training Program
In cooperation with local medical associations and academic societies, the JMA co-hosts seminars such as the “Meeting for Supporting Medical Students and Residents” to promote awareness of employment support for women physicians and others, aiming to help them balance life events with their medical careers. In addition, to ensure learning opportunities for women physicians and others who are raising children, the JMA promotes the establishment of on-site childcare services at training sessions and seminars organized by local medical associations, and provides financial assistance for such services.
Furthermore, to facilitate mutual information exchange between the JMA and local medical associations, the JMA holds “Regional Block Meetings on Support for Women Physicians and Collaboration with the Doctor Bank” in various regions across Japan, along with other related initiatives.
JMA Evaluation Center for the Work Environment of Medical Institutions
In April 2022, the JMA was designated as an Evaluation Center for the Work Environment of Medical Institutions under the Medical Care Act.
Its duties include:
- Publicizing and publicity the work environment evaluation system for medical institutions.
- Evaluating the work management system and work status of physicians in medical institutions, as well as assessing their efforts and results in reducing working hours.
- Providing training for surveyors who conduct evaluations of medical institutions.
- Offering consultation, information, and support for the implementation of work environment evaluation at medical institutions.
Japan Medical Association Research Institute (JMARI)

The Japan Medical Association Research Institute (JMARI) was established to strongly support the “Development of Health Care Policies for the Japanese People” that JMA promotes. It is JMA’s Think Tank. The foremost guiding principle of JMARI is to strive to achieve humane health care. The term “humane” signifies kindness, compassion, and consideration. Still, in this case, it also denotes assurance that stems from the confidence of the professional physician. Humane health care is also easy to understand. The focus of the research conducted by the JMARI is always people oriented.
Mission
The JMARI was established to conduct the following tasks.
-To plan and draft health care policies that the Japanese public will select.
-To create a consensus-building process centered on the Japanese people.
-To provide reliable data and information.
The diverse selection of health care policies that are drafted to fulfill these tasks are used to support JMA activities.
Research Network
JMARI is in the process of establishing the research network system. Opened to the following concerning organizational level.
Research Systems and Fields
Economics and Information
Social Security Policy based on Long-term Vision
Social Security Expense and Inter-Industrial Relationship
Structural Health Care Reform/Medical Fee Reimbursement
Health Information Network
Medical Management
Long-Term Care Insurance System / Long -Term Care Service
Pharmaceutical Marketing System
Physician-Patient Relationship
Bioethics
Medical Ethics
Medicine and Ethics
Physician-Patient Relationship
Bioethics/Medical Ethics
Medical Education / Continuing Medical Education / Technical Innovation
Internationalization and Global Standard
Information Disclosure
Medical Risk Management
Strategy and Development
Good Relationship with Public
Countermeasures against Aging
Countermeasures against Fewer Children
Health Investment
System Development
Promoting Mutual Understanding in Governmental Agencies and Organizations